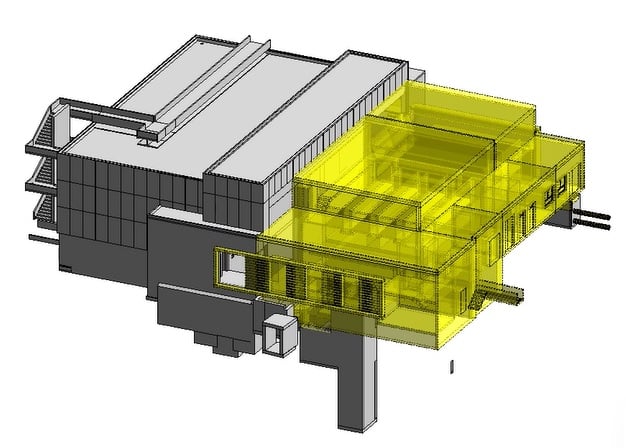
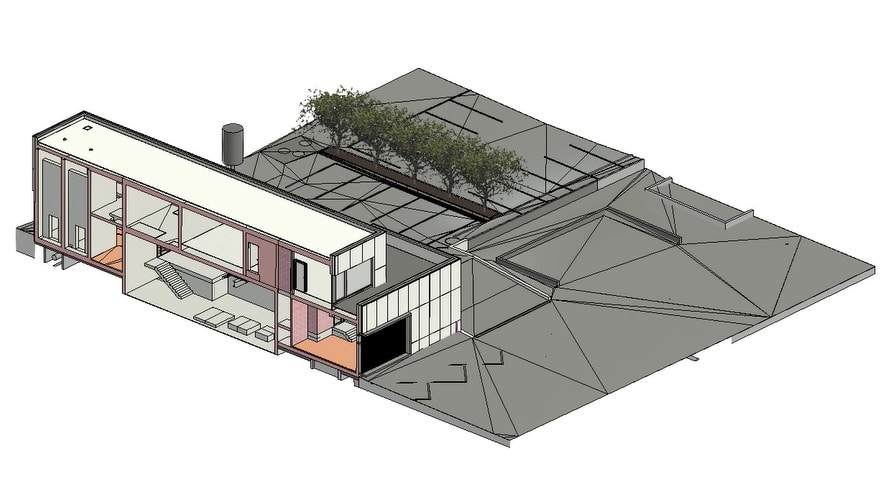
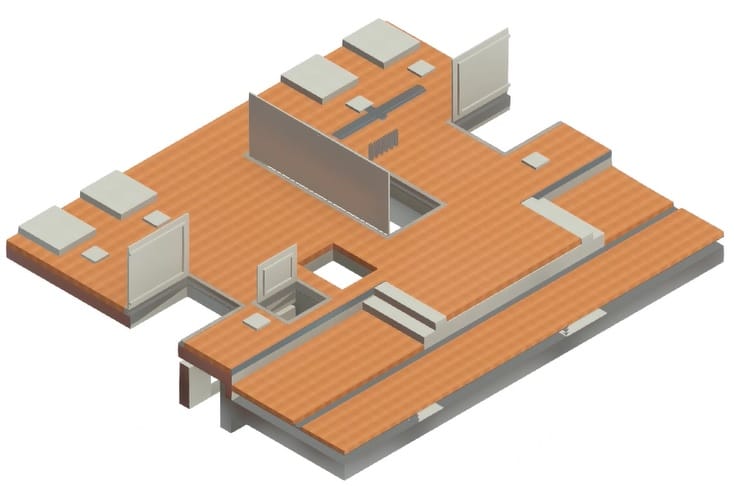
A BIM (Building Information Modeling) digital model is a three-dimensional digital representation of a building or infrastructure that integrates all the data related to its design, construction, and management throughout its lifecycle. It is created using BIM modeling software that allows the creation of intelligent objects containing detailed information about building elements such as walls, doors, windows, electrical and plumbing installations, etc.
This BIM digital model can be used by all stakeholders involved in the project, such as architects, engineers, contractors, owners, and infrastructure managers. They can access it to collaborate on the design, construction, and management of the project. The BIM digital model allows for improved coordination and collaboration among different stakeholders, avoiding interference conflicts and reducing delays and costs.
Moreover, the BIM digital model can be used to simulate the building’s energy performance, assess its environmental impact, perform cost and planning analyses, and facilitate maintenance and facility management.
In summary, the BIM digital model is a comprehensive and detailed digital representation of a building or infrastructure that allows for effective coordination and collaboration among stakeholders throughout the lifecycle of the project.
Objectives of a BIM digital model
Working with the BIM method should first and foremost allow for achieving general priority objectives:
- Improved planning quality and safety through enhanced content and quantity/dimension overviews and automated control of planning data consistency.
- Planning assistance through improved communication and visualizations.
- Improved profitability and reduced lifecycle costs of the project through better management control, simulations, and specific data checks.
- Assistance in operational and usage planning of the project by reviewing usage-specific aspects and project-specific company guidelines.
- Consideration of social and environmental aspects through data control, e.g., regarding sustainability and accessibility guidelines.
- Assistance in tendering and construction phases.
Necessary steps to produce a BIM digital model
- Data collection and creation: Data can be collected from plans, laser surveys, existing 3D models, or any other visual support. Data must be organized and verified to ensure accuracy and integrity.
- Digital model creation: The data is then used to create the BIM digital model using BIM software. Modeling involves creating intelligent objects that contain information such as dimensions, materials, physical properties, and performance data.
- Digital model coordination: The different object models created by different stakeholders are coordinated to ensure they do not present any interferences. This step detects and resolves potential conflicts that could result in errors or delays during construction.
- Information addition: Additional information is added to the BIM digital model, such as costs, schedules, energy and environmental analyses, management and maintenance information, etc.
- Use of the BIM digital model: The BIM digital model can be used for various purposes, such as design, planning, construction, management, maintenance, cost and time analysis, etc. It is often shared with all stakeholders involved in the project for better collaboration.
Types of digital models
It may be wise to work on a BIM project with models from the following specialists:
- Architecture model: in general, the architecture model is the reference model in which the basic design, as well as the floors and spaces, are established. The basic structure is predefined for the data model.
- Civil engineer model: partial models for supporting structures, regulated areas, and possibly reinforcements.
- Building services model: HVAC/electrical/plumbing/lighting models, as well as partial models of openings/reservations in buildings.
- Urban and land models: extracted as an existing model and for landscape models, digital terrain models.
Our team of geomaticians and modellers has expertise gained since the beginning of BIM for the production of digital models.
Production of an existing digital model
In the context of renovation, the analysis of old plans often presents differences with a building. Conformant plans are rare, and documentation of changes made over time is often non-existent.
A 3D laser scan survey allows for the rapid measurement of the entire building. Read 3D laser scan.
Based on archive plans and the georeferenced point cloud, the Newis team provides strong expertise for the design of architecture/civil engineering and equipment models.