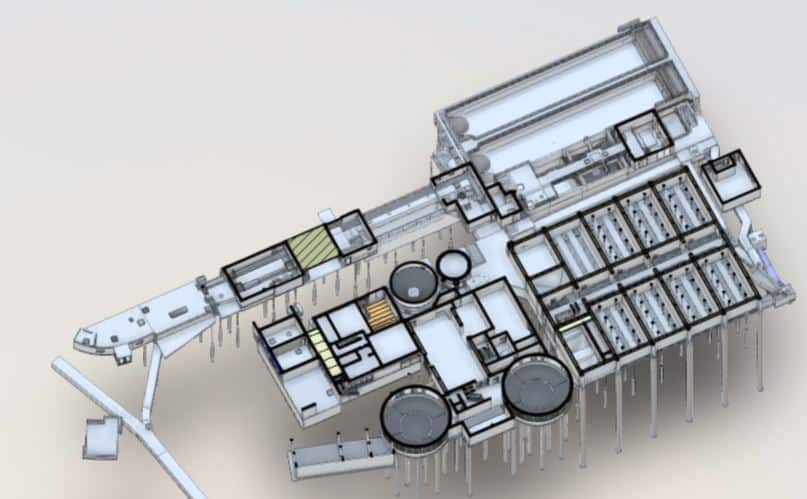
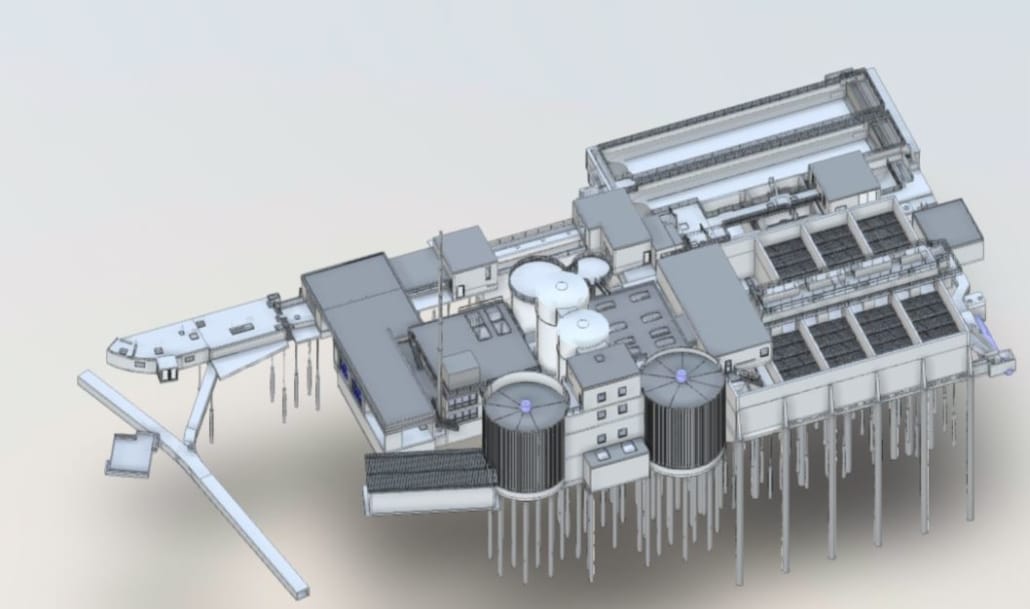
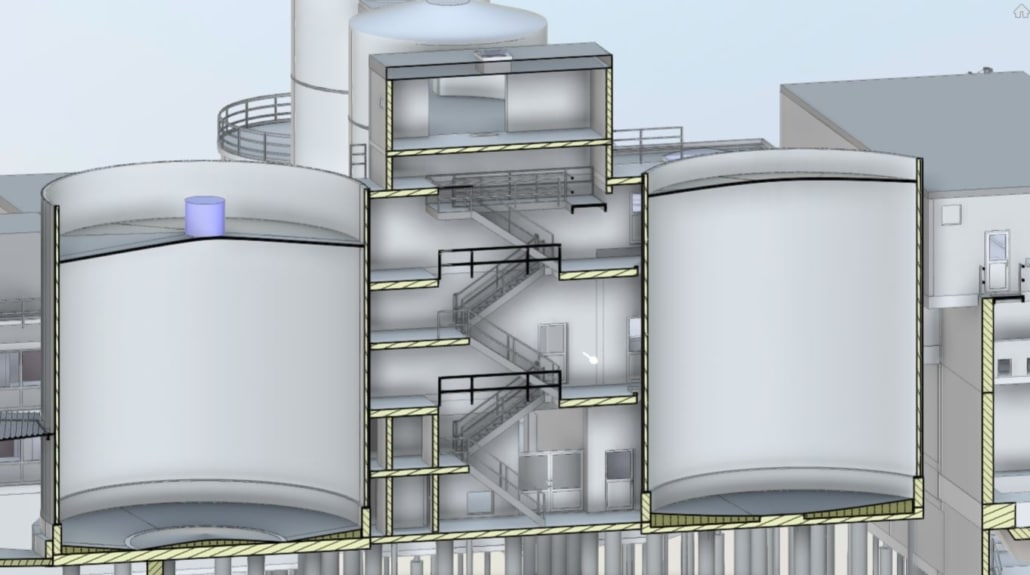
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a process of designing, constructing, and managing projects using 3D digital models to represent the physical and functional characteristics of a building or infrastructure.
The dimensions of BIM refer to the different phases of project development and management.
BIM dimensions are generally classified into four levels, also called “dimensions”:
- BIM 3D – three-dimensional representation of the structure: The first dimension is 3D modeling, which involves creating a three-dimensional digital representation of the building or infrastructure. 3D models allow for viewing the structure from different angles and better understanding its geometry.
- BIM 4D – analysis of construction time: The second dimension is 4D modeling, which integrates the time dimension. This dimension allows for planning and simulating the different stages of the project, using calendars and Gantt charts to schedule tasks and activities.
- BIM 5D – cost analysis: The third dimension is 5D modeling, which integrates the cost dimension. This dimension allows for associating elements of the 3D model with specific costs, to obtain a more accurate estimate of construction and maintenance costs.
- BIM 6D – sustainability assessment: The fourth dimension is 6D modeling, which integrates the sustainability dimension. This dimension allows for analyzing the environmental and energy performance of the building or infrastructure, using simulation tools to evaluate energy consumption, carbon emissions, and energy efficiency.
- BIM 7D – Facility Management Phase: 7D corresponds to the operational management and maintenance of the building and its components throughout its lifecycle. It is used to track important asset data such as its condition, maintenance and operating manuals, warranty information, technical specifications, etc., for future use. BIM 7D allows for optimized management of facilities and their installations from design to demolition, and simplifies the audit and maintenance processes of the facility and its components.
In addition to the 7 regulated dimensions, there are now three “new dimensions of BIM”: 8D which concerns safety assurance in the design and construction phase of the facility, 9D which corresponds to Lean Construction, and 10D which focuses on the industrialization of construction.
In summary, the dimensions of BIM refer to the different phases of the project design and management process, which use 3D digital models to represent the physical and functional characteristics of a building or infrastructure. These dimensions integrate temporal, financial, and environmental aspects to improve project planning, construction, and management.